PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 03 outubro 2024
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/76d00455660f8d0dfa42fcd70278635b6c0e6ff5/1-Figure1-1.png)
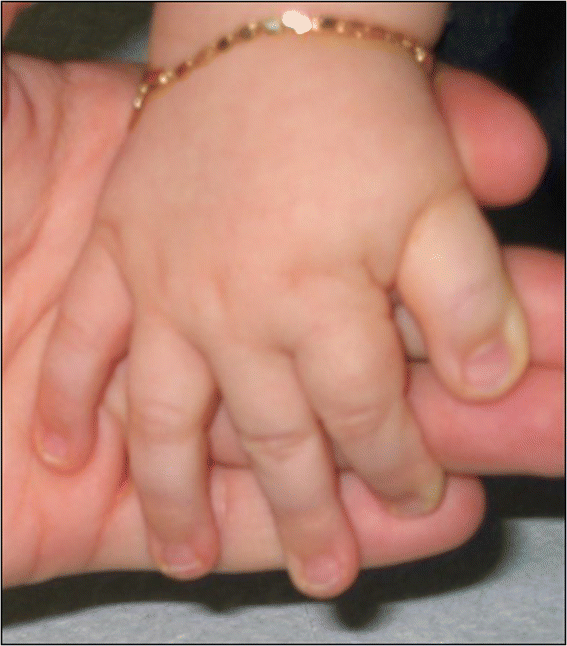
A typical six-month-old girl with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome was presented with typical facial changes including downward-sloping palpebral fissures, prominent forehead, hypertelorism, limited mouth opening, large beaked nose, and high arched palate. Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome (RTS) was first described by Michail et al[1] and subsequently by Rubinstein and Taybi[2]. We present a typical six-month-old girl with RTS. Her mother had ovarian cancer and polyhydramnios during the pregnancy. Parents are closely related. There were frequent respiratory infections resulting in two hospital admissions. Physical examination revealed typical facial changes including downward-sloping palpebral fissures, prominent forehead, hypertelorism, limited mouth opening, large beaked nose, and high arched palate (Fig. 1). A history of increased tearing was compatible with nasolacrimal duct obstruction. Other features include general hypotonia with delayed developmental milestones, short and broad thumbs and toes (Fig. 1). Chest x-ray showed cardiomegaly (Fig. 2). She had normal karyotype.
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://www.ahajournals.org/cms/asset/a6672ae3-8d0f-4b81-a312-1cbfe4d5a5c3/jah37672-fig-0004.png)
Patent Ductus Arteriosus: A Contemporary Perspective for the Pediatric and Adult Cardiac Care Provider
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/615919/fped-08-615919-HTML/image_m/fped-08-615919-g002.jpg)
Frontiers Transcatheter Closure of Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Premature Infants With Very Low Birth Weight
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/615919/fped-08-615919-HTML/image_m/fped-08-615919-g001.jpg)
Frontiers Transcatheter Closure of Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Premature Infants With Very Low Birth Weight
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/23617ae5de57698a16f51313ff821d46e487f2c2/7-Table7-1.png)
PDF] Percutaneous Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) Closure in Very Preterm Infants: Feasibility and Complications
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://f6publishing.blob.core.windows.net/a7a9dd9c-137e-4223-8b63-2a1ab9b60b69/WJC-14-54-g001.png)
Anesthetic management of a child with Cornelia de Lange Syndrome undergoing open heart surgery: A case report
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://rc.rcjournal.com/content/respcare/67/5/594/F1.large.jpg)
Definitive Closure of the Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Preterm Infants and Subsequent Short-Term Respiratory Outcomes
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://ars.els-cdn.com/content/image/1-s2.0-S1875213610001555-gr3.jpg)
The ductus arteriosus: Physiology, regulation, and functional and congenital anomalies - ScienceDirect
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://media.springernature.com/m685/springer-static/image/art%3A10.1038%2Fs41372-019-0506-7/MediaObjects/41372_2019_506_Fig1_HTML.png)
Patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants: is early transcatheter closure a paradigm shift?
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Mehmet-Ergun/publication/23239728/figure/fig1/AS:310579593007105@1451059353870/Characteristic-facial-appearance-with-downward-slant-of-palpebral-fissure-mild_Q320.jpg)
PDF) Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome with normal FISH result and CREBBP gene analysis: A case report
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://i1.rgstatic.net/ii/profile.image/272355641524252-1441946053706_Q64/Keyhan-Zanjani-2.jpg)
PDF) Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://www.ahajournals.org/cms/asset/ba8d72f9-9a56-444e-ad58-f6ca521ab64f/hc2392821004.jpeg)
Char Syndrome, an Inherited Disorder With Patent Ductus Arteriosus, Maps to Chromosome 6p12-p21
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://media.springernature.com/m685/springer-static/image/art%3A10.1038%2Fs41598-019-52936-6/MediaObjects/41598_2019_52936_Fig1_HTML.png)
Characteristics of Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Congenital Rubella Syndrome
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://i1.rgstatic.net/publication/262940679_Patent_Ductus_Arteriousus_Device_Closure_in_an_Infant_with_Rubinstein-Taybi_Syndrome/links/5497d7a90cf2ec13375d43ae/largepreview.png)
PDF) Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://europepmc.org/articles/PMC7605084/bin/PEDS_20201209_f1.jpg)
Patent Ductus Arteriosus of the Preterm Infant. - Abstract - Europe PMC
Recomendado para você
-
 A case with Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: A novel frameshift mutation03 outubro 2024
A case with Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: A novel frameshift mutation03 outubro 2024 -
 Born with Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome (RTS), Braxton and Family are03 outubro 2024
Born with Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome (RTS), Braxton and Family are03 outubro 2024 -
DBMCI MDS : Formerly MDS Experts - RUBINSTEIN TAYBI SYNDROME An03 outubro 2024
-
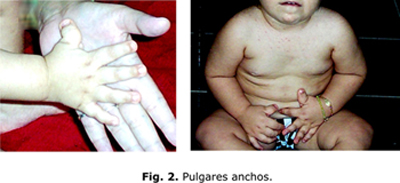 Síndrome de Rubinstein-Taybi03 outubro 2024
Síndrome de Rubinstein-Taybi03 outubro 2024 -
 Síndrome de rubinstein taybi - canalSALUD03 outubro 2024
Síndrome de rubinstein taybi - canalSALUD03 outubro 2024 -
ALPI Rafaela - 🔹 Día Mundial del Síndrome de Rubinstein03 outubro 2024
-
 Síndrome de Cornelia de Lange Síndrome Cri du chat Síndrome de Rubinstein – Taybi03 outubro 2024
Síndrome de Cornelia de Lange Síndrome Cri du chat Síndrome de Rubinstein – Taybi03 outubro 2024 -
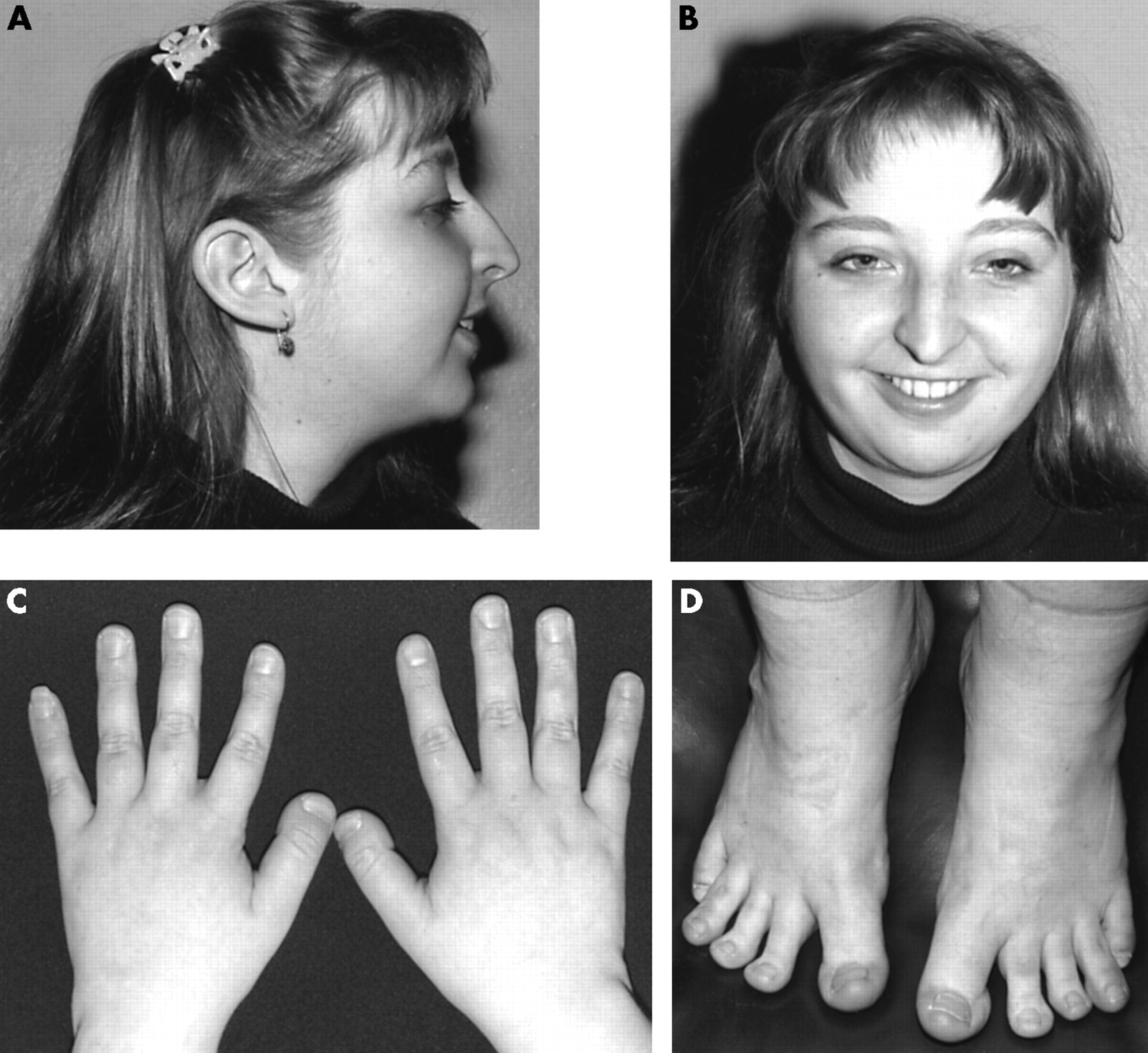 Molecular studies in 10 cases of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome, including a mild variant showing a missense mutation in codon 1175 of CREBBP03 outubro 2024
Molecular studies in 10 cases of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome, including a mild variant showing a missense mutation in codon 1175 of CREBBP03 outubro 2024 -
 Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: clinical features, genetic basis, diagnosis, and management, Italian Journal of Pediatrics03 outubro 2024
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: clinical features, genetic basis, diagnosis, and management, Italian Journal of Pediatrics03 outubro 2024 -
 High frequency of copy number imbalances in Rubinstein–Taybi03 outubro 2024
High frequency of copy number imbalances in Rubinstein–Taybi03 outubro 2024
você pode gostar
-
 Evade Tryhard x Red Cashier03 outubro 2024
Evade Tryhard x Red Cashier03 outubro 2024 -
 Cinco novas especializações técnicas estão disponíveis nas Etecs03 outubro 2024
Cinco novas especializações técnicas estão disponíveis nas Etecs03 outubro 2024 -
Joker's Sport Bar - Se tem final da NBA, tem transmissão no Joker´s! ⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀ 🏀O Phoenix Suns abriu 2 a 0 nas Finais da NBA mas a equipe do Milwaukee Bucks não03 outubro 2024
-
 Top 74 Similar websites like freegamesland.net and alternatives03 outubro 2024
Top 74 Similar websites like freegamesland.net and alternatives03 outubro 2024 -
 Sad Trollface Blank Template - Imgflip03 outubro 2024
Sad Trollface Blank Template - Imgflip03 outubro 2024 -
 Campeonato Brasileiro: como assistir Palmeiras x América-MG online gratuitamente03 outubro 2024
Campeonato Brasileiro: como assistir Palmeiras x América-MG online gratuitamente03 outubro 2024 -
 Crossdressing pandemic has just the best traps <3 : r/CuteTraps03 outubro 2024
Crossdressing pandemic has just the best traps <3 : r/CuteTraps03 outubro 2024 -
 Steam - Steam passa a oferecer reembolso para jogos, DLC e itens - The Enemy03 outubro 2024
Steam - Steam passa a oferecer reembolso para jogos, DLC e itens - The Enemy03 outubro 2024 -
 Dr. Dre - 2001, Album Cover Poster For Wall Art, Home Decor sold by Ibrahim Fawzi, SKU 4109054503 outubro 2024
Dr. Dre - 2001, Album Cover Poster For Wall Art, Home Decor sold by Ibrahim Fawzi, SKU 4109054503 outubro 2024 -
 F1 Racing Tapestry Banner para dormitório estudantil, cabeceira, carro legal, clube, estudante03 outubro 2024
F1 Racing Tapestry Banner para dormitório estudantil, cabeceira, carro legal, clube, estudante03 outubro 2024


